数独
分析
见《进阶指南》第102页。
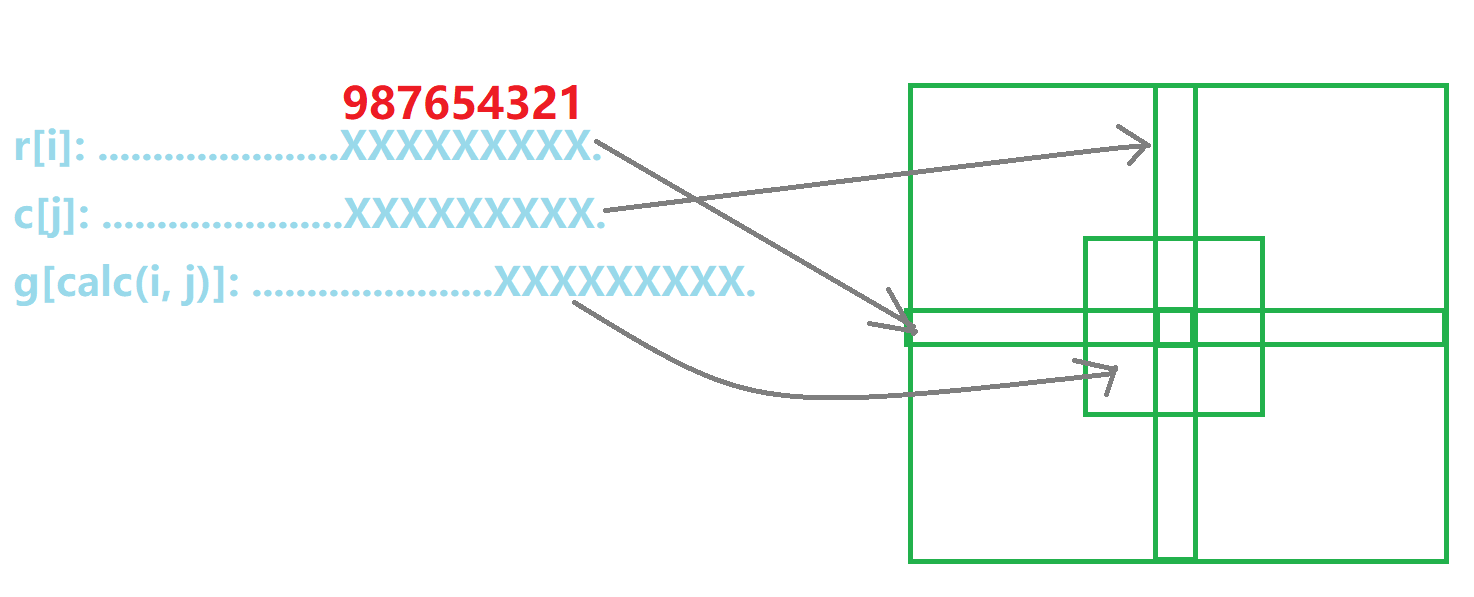
实现
#include <iostream>
#define log2 LoG2
using namespace std;
const int N = 10, M = 512;
char a[N][N];
int r[N], c[N], g[N];
int popcount[M], log2[M];
int pos (int i, int j) {
return 3 * (i / 3) + j / 3;
}
void flip (int i, int j, int k) {
r[i] = r[i] ^ (1 << k);
c[j] = c[j] ^ (1 << k);
g[pos(i, j)] = g[pos(i, j)] ^ (1 << k);
}
int lowbit (int x) {
return x & -x;
}
bool dfs (int cnt) {
if (cnt == 0) return true;
int temp = 10, x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++ i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; ++ j) {
if (a[i][j] == '.') {
int val = r[i] & c[j] & g[pos(i, j)];
if (val == 0) return false;
if (popcount[val] < temp) {
temp = popcount[val];
x = i, y = j;
}
}
}
}
for (int val = r[x] & c[y] & g[pos(x, y)]; val >= 1; val -= lowbit(val)) {
int k = log2[lowbit(val)];
a[x][y] = k + '1';
flip(x, y, k);
if (dfs(cnt - 1) == true) return true;
flip(x, y, k);
a[x][y] = '.';
}
return false;
}
int main () {
for (int i = 0; i < (1 << 9); ++ i)
for (int j = i; j >= 1; j -= lowbit(j))
++ popcount[i];
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++ i) log2[1 << i] = i;
string str;
while (cin >> str && str != "end") {
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); ++ i)
a[i / 9][i % 9] = str[i];
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++ i)
r[i] = c[i] = g[i] = (1 << 9) - 1;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++ i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; ++ j) {
if (a[i][j] == '.') {
++ cnt;
} else {
flip(i, j, a[i][j] - '1');
}
}
}
dfs(cnt);
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++ i)
for (int j = 0; j < 9; ++ j)
cout << a[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
